types of vaccine delivery system
Messenger RNA mRNA vaccine. Vaccine delivery systemseg emulsions microparticles immune-stimulating complexes ISCOMs liposomes.

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine
Sonophoresis is a technique that uses ultrasound to permeabilize the stratum corneum layer of the skin.

. Microneedle arrays are one example of a new method to deliver medications through the skin. New developments in vaccine delivery systems will improve the efficiency of clinical trials in the near future. Recent decades have brought major advances in understanding the complex interactions between the microbes.
21 251259 2013. Or being studied include. Recommended Childhood ages 0-6 Immunization.
There are many types of vaccines categorized by the antigen used in their preparation. An mRNA vaccine or RNA vaccine is a novel type of vaccine which is composed of the nucleic acid RNA packaged within a vector such as lipid nanoparticles. Vaccine suspension of weakened killed or fragmented microorganisms or toxins or other biological preparation such as those consisting of antibodies lymphocytes or messenger RNA mRNA that is administered primarily to prevent disease.
Types of Vaccine Live attenuated LAV Inactivated killed antigen Subunit purified antigen Toxoid. With one exception distribution and delivery of COVID-19 vaccines and other routine vaccines are accomplished through a federal delivery system. This review mainly discusses non-viral vectors which can be further subdivided into lipid or lipid materials and polymer delivery systems.
To overcome these hurdles an efficient vaccine delivery system is required which not only delivers the vaccine molecules to the target site to evoke enduring immune responses but also has minimal side effects and requires less doses. The common routes of vaccine delivery are parenteral injection needle-free injections intranasal ocular oral and spray topical. Immunostimulatory adjuvantsConserved molecular patterns of pathogen.
The size of the particle systems influences cellular targeting. Moreover there is an increasing need to develop new generation composite vaccine molecules that will act as. Dime-sized patch of dissolvable microneedles for self-administration of influenza vaccine.
Intradermal Delivery of Vaccines Executive summary The dermis and epidermis of the human skin are rich in antigen-presenting cells. Improving current delivery methods or designing new ones can enhance the use of existing medications. Techniques such as sonophoresis microneedle-assisted delivery iontophoresis and elastic liposomes are among those being used and developed for transdermal vaccine delivery.
Most vaccine delivery systems are particulate including nanoparticles microparticles or adjuvant-formulated proteins. Miniaturizing the vaccine delivery system also reduces the burden on the so-called cold chain a baton race from manufacturing plant to patient arm through a series of special refrigerated trucks and shipping containers designed to keep vaccines at. Concerted efforts by researchers on alternative vaccine delivery routes have yielded a range of novel delivery devices with potential to enhance immunogenicity and stability.
This type of vaccine uses genetically engineered mRNA to give your cells instructions for how to make the S protein found on the surface of the COVID-19 virus. Delivering COVID-19 vaccines. DNA vaccinesplasmids can be administered to the animals by one of the following delivery method.
Thus new adjuvants or self-adjuvanting vaccine delivery systems are required. Microneedles have been used to successfully administer a variety of vaccine types including viral vector DNA protein peptide virus-like particles nanoparticle vaccines and attenuated or inactivated viruses with or without adjuvants. Type I IFN counteracts the induction of antigen-specific immune responses by lipid-based delivery of mRNA vaccines.
Replicating Replicating viral vectors retain the ability to make new viral particles alongside delivering the vaccine antigen when used as a. Pfizer distributes and delivers doses of its COVID-19 vaccine through its own delivery system. The main types of COVID-19 vaccines currently available in the US.
In particular they describe novel polymeric microneedle. Scientific research has led to the development of numerous types of vaccines that safely elicit immune responses that protect against infection and researchers continue to investigate novel vaccine strategies for prevention of existing and emerging infectious diseases. Delivery systems for mRNA vaccines can be divided into viral- and non-viral vector delivery systems.
The globally recommended vaccines discussed in this module fall into four main types. Vaccines of this type on US. Among the COVID-19 vaccines are a number of RNA vaccines under development to combat the COVID-19 pandemic and some have been approved or have received emergency use authorization in some countries.
Their formulations affect how they are used how they are stored and how they are administered. Among them nanoparticles NPs such as dendrimers polymeric NPs metallic NPs magnetic NPs and quantum dots have emerged as effective vaccine adjuvants for infectious diseases and cancer therapy. After vaccination your muscle cells begin making the S protein.
The most extensively studied is the influenza vaccine but vaccines for hepatitis B hepatitis C. Viral vectored vaccines are significantly cheaper to produce in most cases compared to nucleic acid vaccines and many subunit vaccines. Here we proposed a self-adjuvanting delivery system that is fully defined biodegradable and non-toxic.
In this Special Focus experts in the field describe recent innovations in the design evaluation and use of novel vaccine delivery devices and systems. More information for how COVID-19 vaccines get to you. Gene gun or biolistic delivery requires nanogram level of plasmids Figure 2Principal of a DNA Vaccine.
This photo shows a r esponder at an. Examples of vaccine delivery systems include liposomes emulsions and microparticles. It has been proposed that delivery of vaccine antigens to these tissues ie intradermal delivery rather than to muscle or subcutaneous tissue could therefore induce superior protective immune.
In order to induce an effective protective immunity these vaccines require boosting with agents called adjuvants. 5 rows Vaccine type. We will discuss each of these briefly in the following slides.
The system is produced by conjugation of polyleucine to peptide antigen followed by self-assembly of the conjugate into nanoparticles.
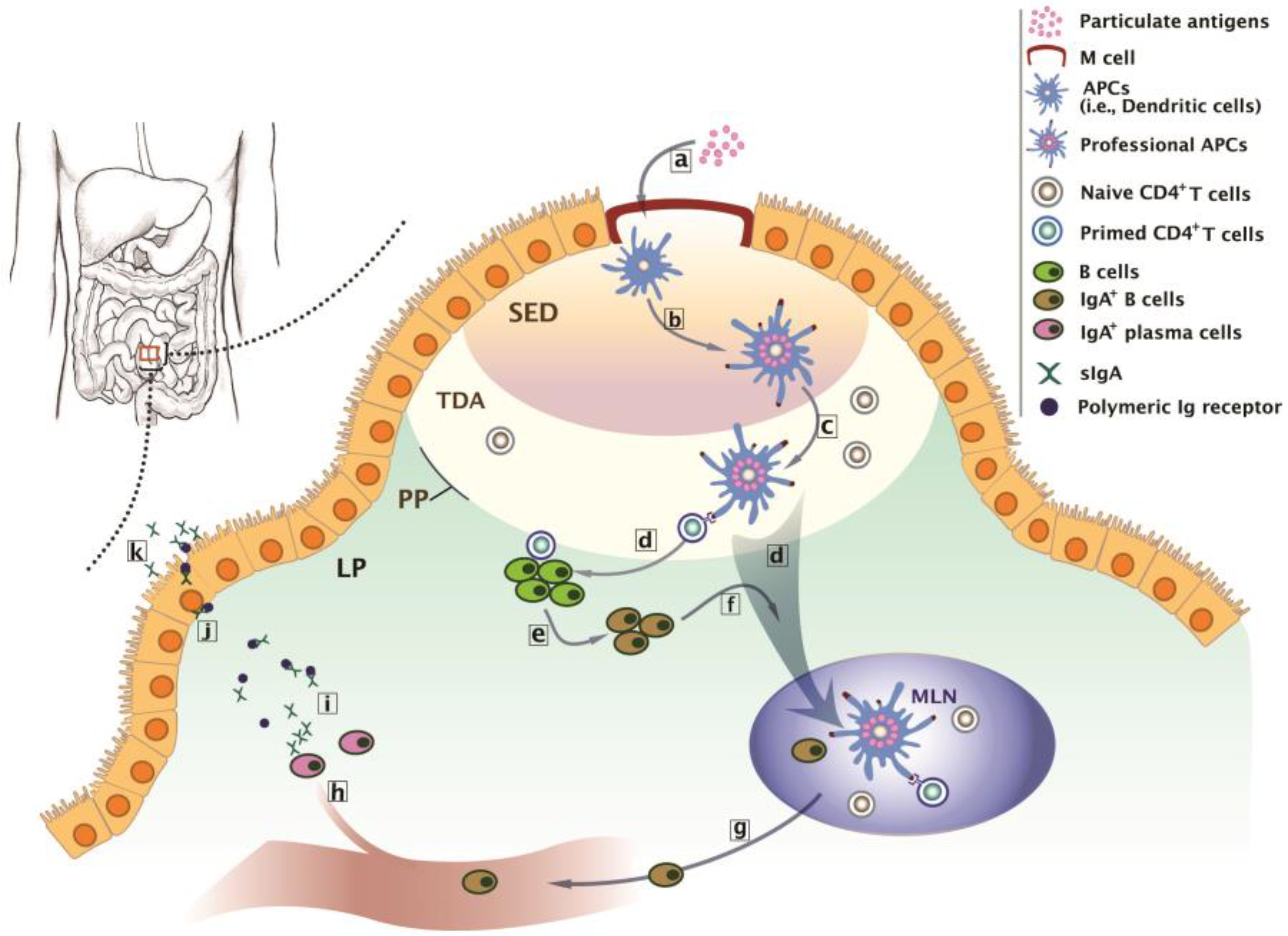
Polymers Free Full Text Oral Vaccine Delivery For Intestinal Immunity Biological Basis Barriers Delivery System And M Cell Targeting Html

How The Sinovac Covid 19 Vaccine Works The New York Times
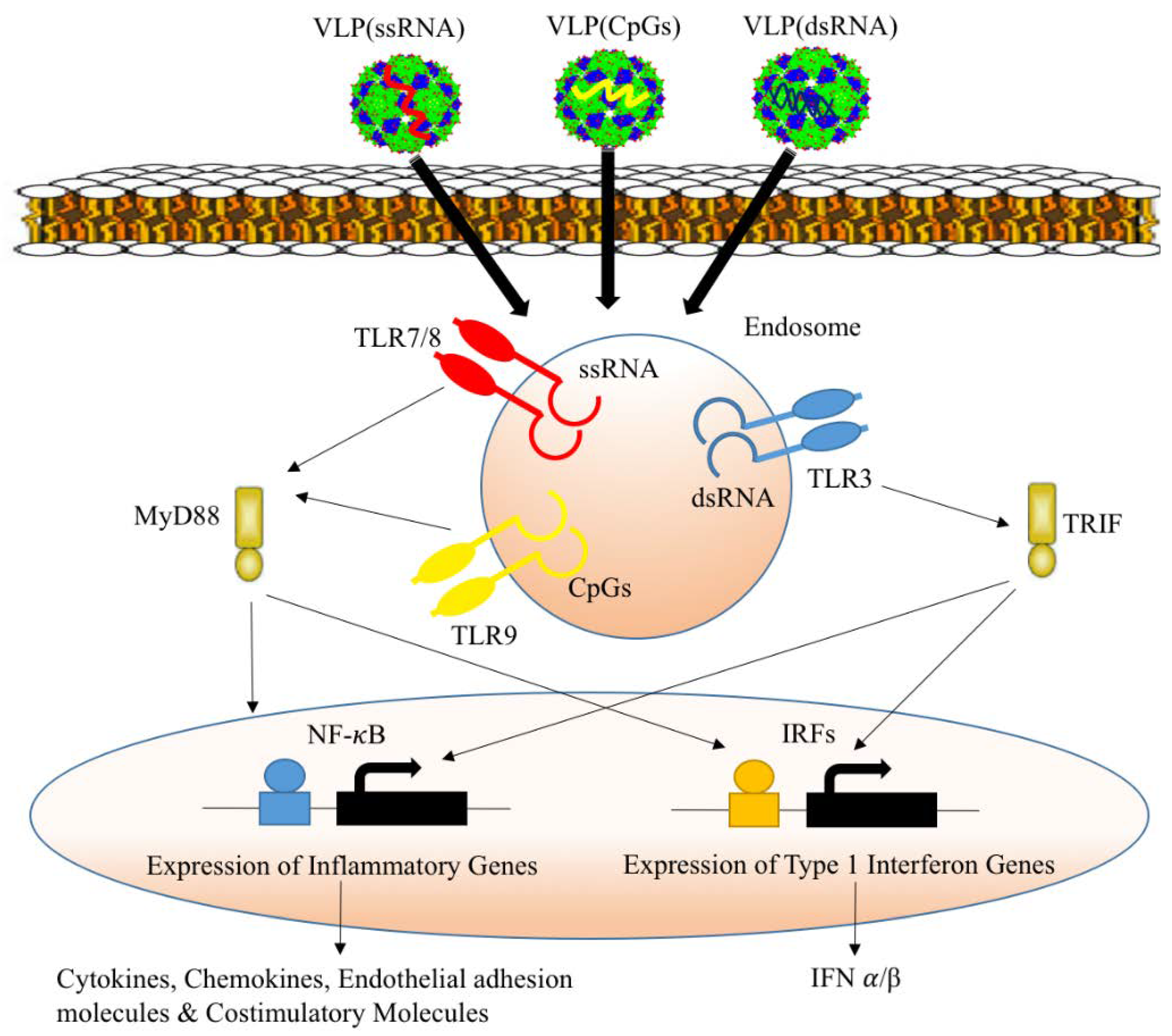
Vaccines Free Full Text Interaction Of Viral Capsid Derived Virus Like Particles Vlps With The Innate Immune System Html
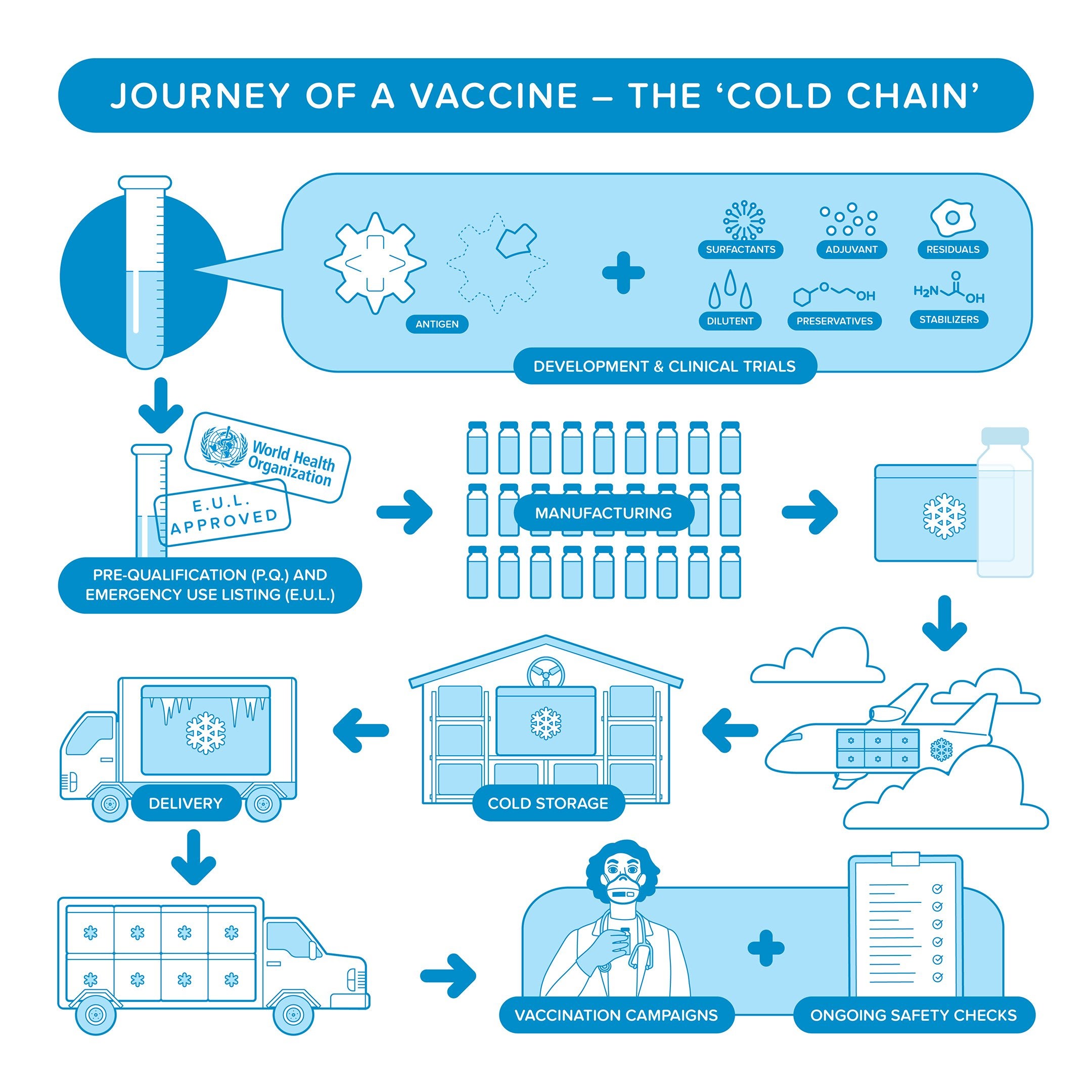
Cold Chain Paho Who Pan American Health Organization

States Are Getting Ready To Distribute Covid 19 Vaccines What Do Their Plans Tell Us So Far Kff

All Types Of Covid 19 Vaccines How They Work Animation Youtube
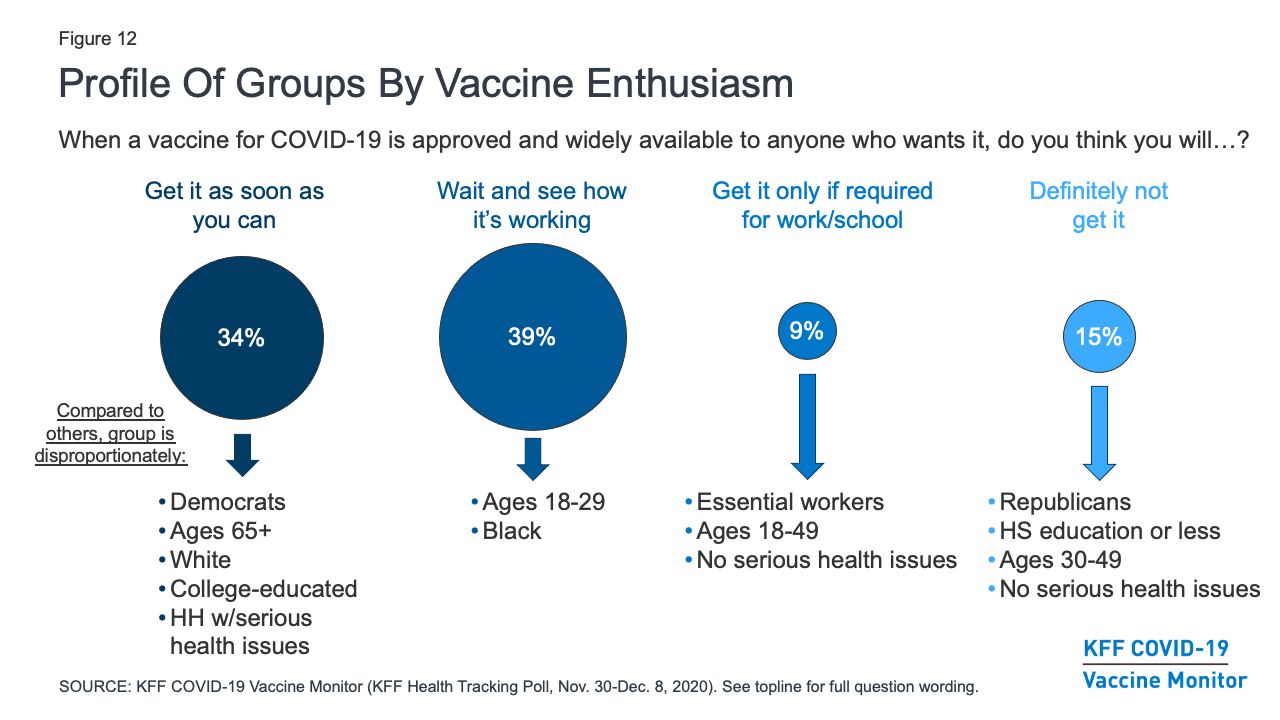
Kff Covid 19 Vaccine Monitor December 2020 Kff
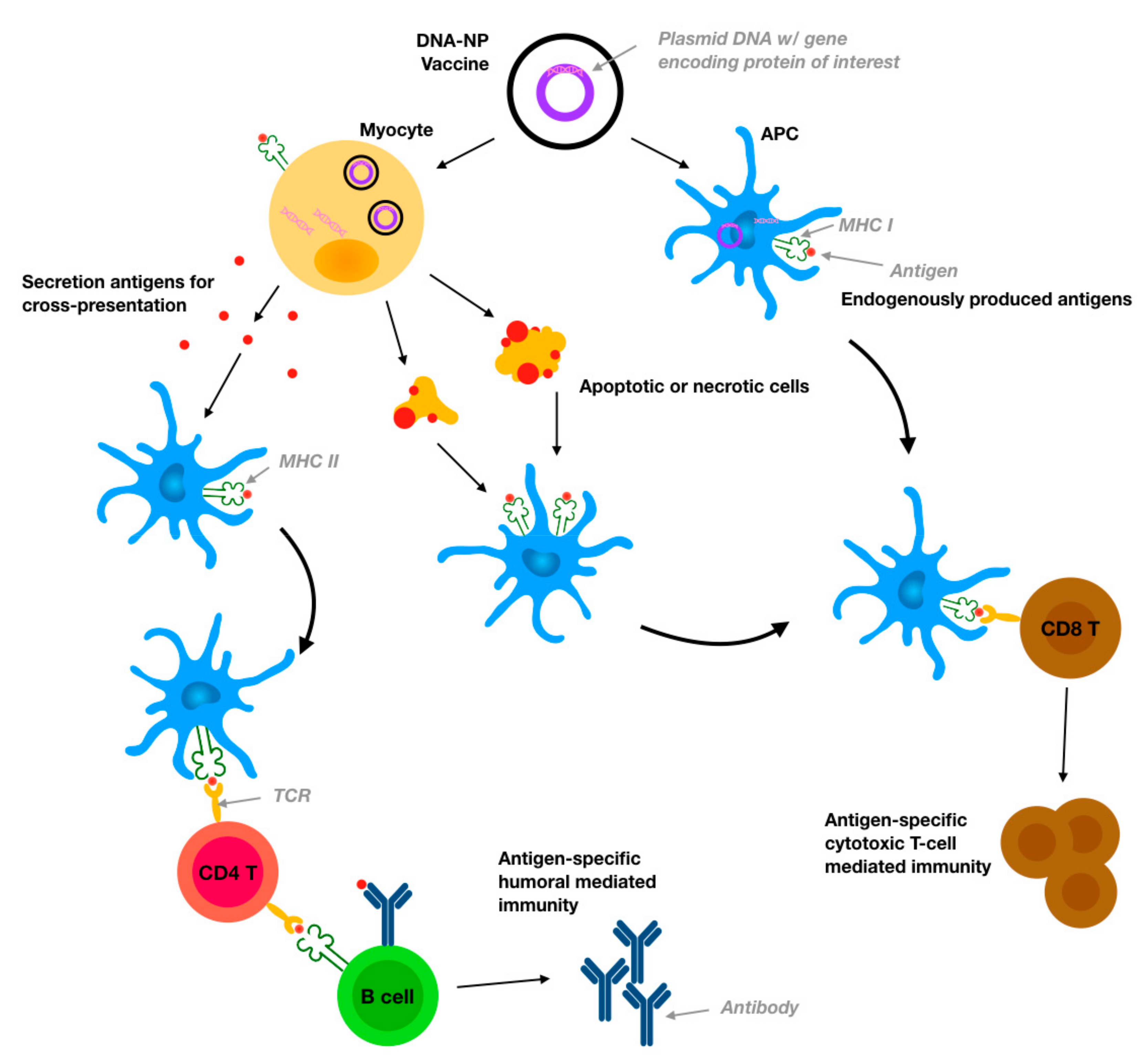
Pharmaceutics Free Full Text Engineered Nanodelivery Systems To Improve Dna Vaccine Technologies Html
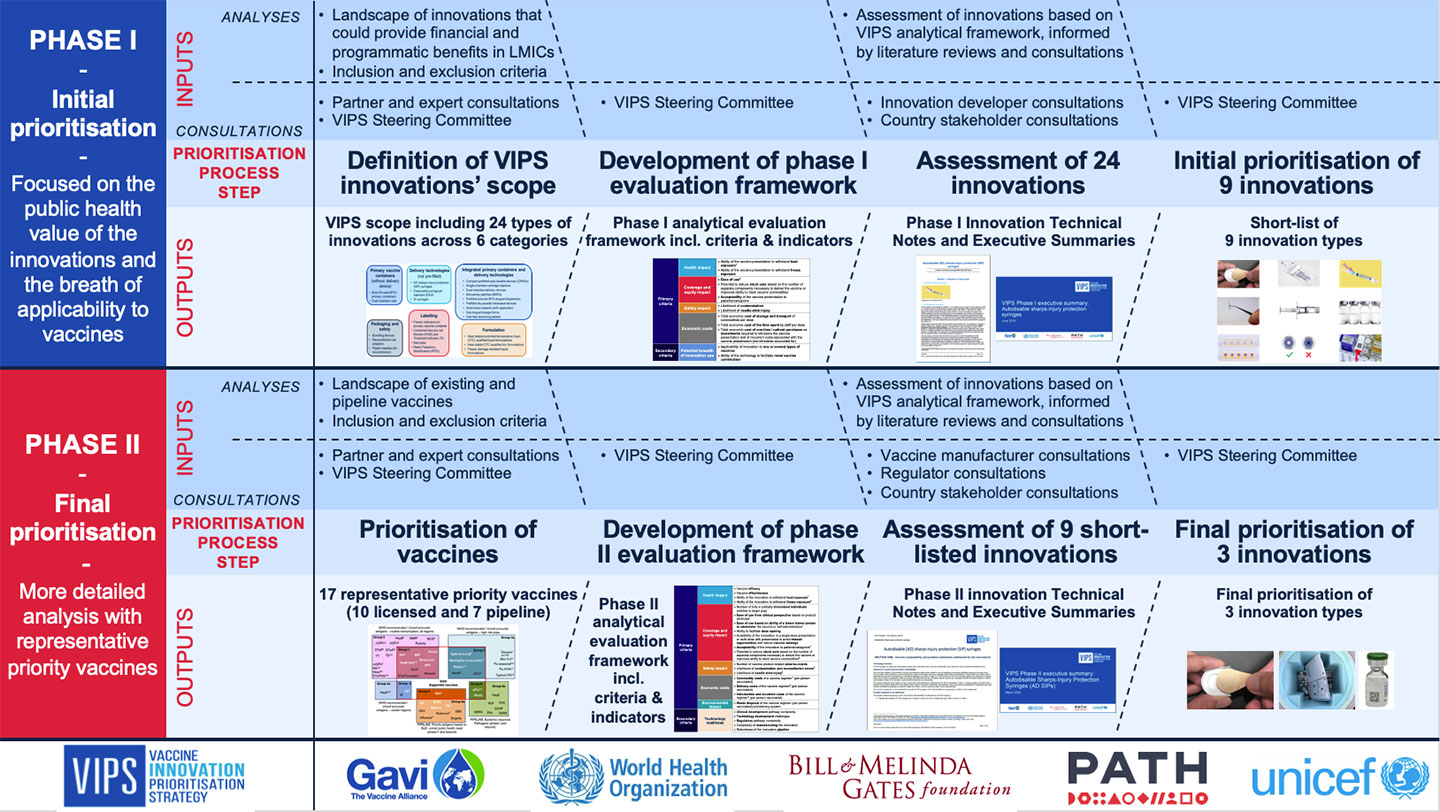
The Vaccine Innovation Prioritisation Strategy

Virosome An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
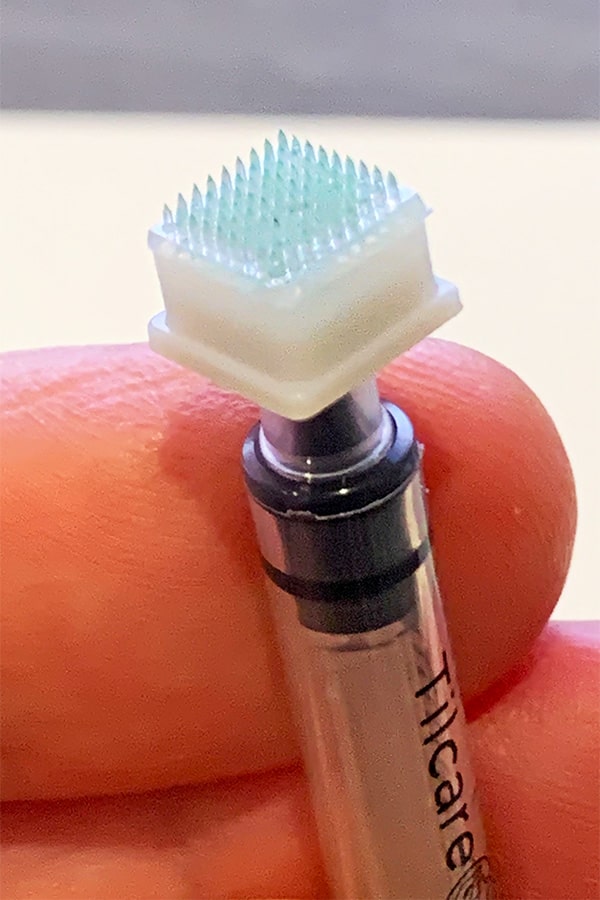

Improving A Vaccine Delivery System For Covid And Beyond
Improving A Vaccine Delivery System For Covid And Beyond
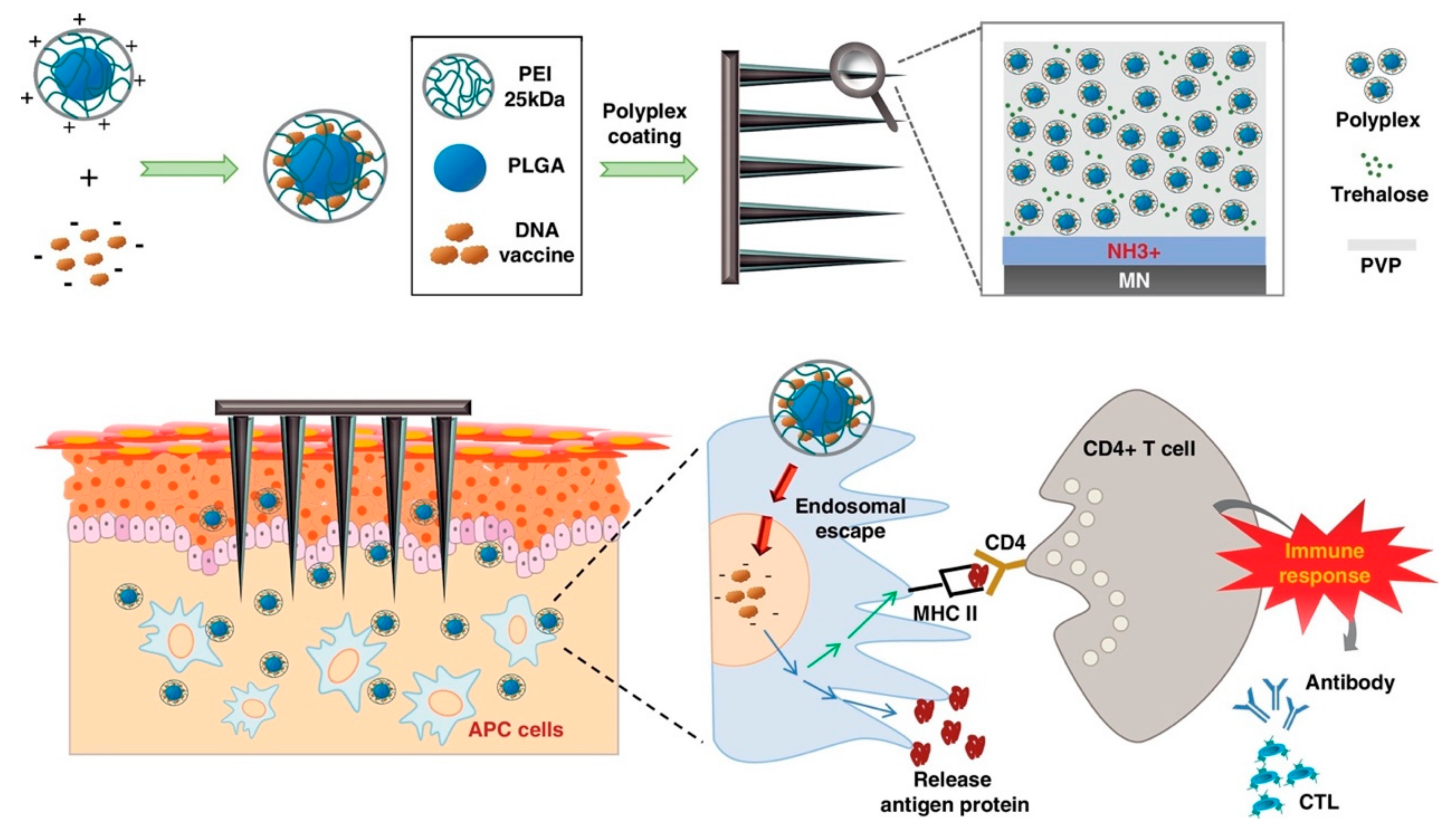
Pharmaceutics Free Full Text Engineered Nanodelivery Systems To Improve Dna Vaccine Technologies Html
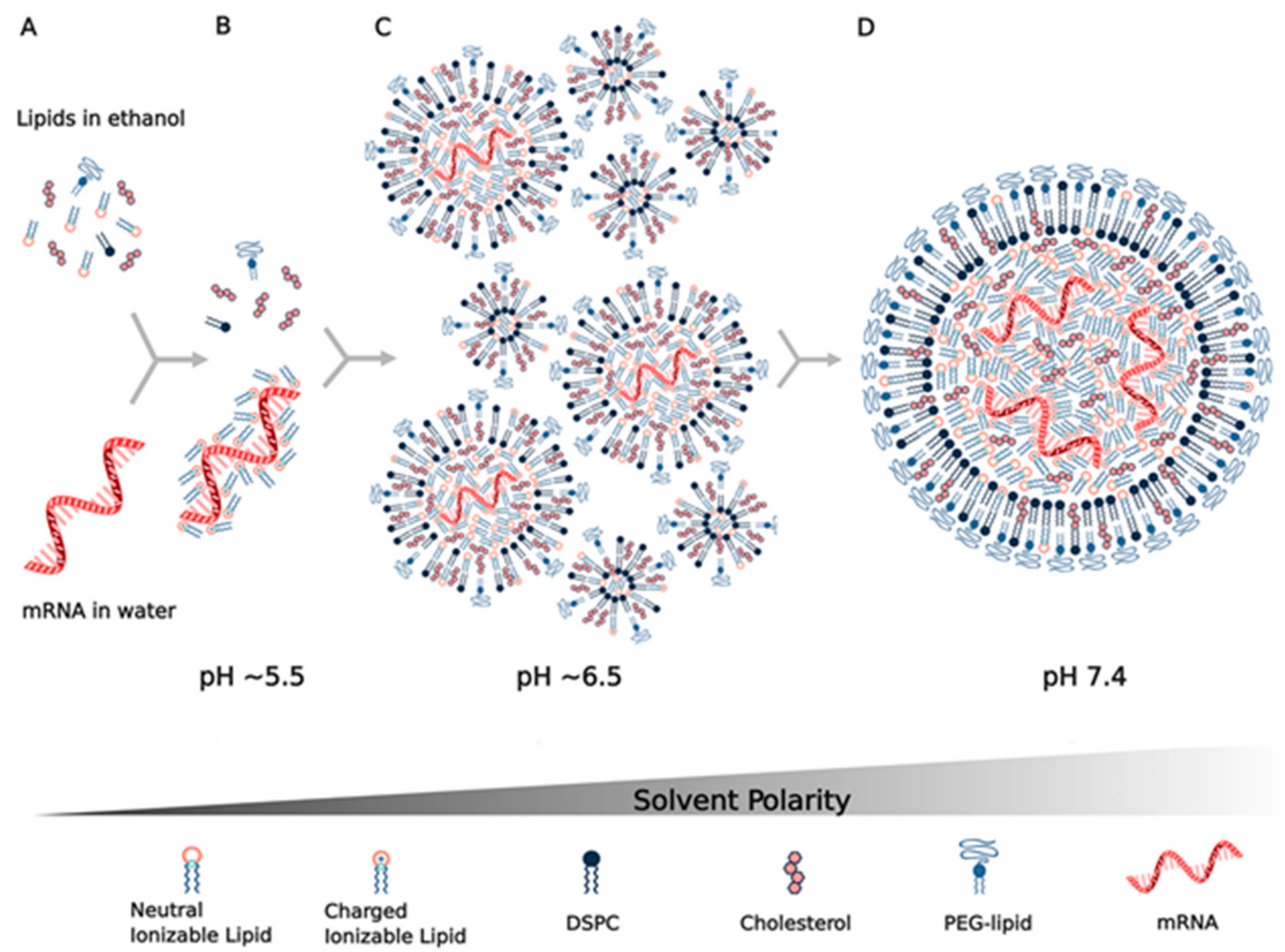
Vaccines Free Full Text Nanomaterial Delivery Systems For Mrna Vaccines Html

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine

Building A Covid 19 Vaccine Verification Solution On Aws Aws For Industries

How The Pfizer Biontech Covid 19 Vaccine Works The New York Times

Polymers Free Full Text Oral Vaccine Delivery For Intestinal Immunity Biological Basis Barriers Delivery System And M Cell Targeting Html